For adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn’s disease (CD).
Demonstrated efficacy
in ulcerative colitis
Results U Need

Lasting relief
and CS-free
remission at Week 521*

Rapid symptom relief as early as Week 61*

Superior to Humira® in clinical remission at Week 52 in
the overall population2,3†‡
Individual results may vary.
*Many patients taking ENTYVIO IV achieved remission at Week 52 vs placebo, some without steroids. Some achieved remission at Week 6. Clinical remission was defined as UC complete Mayo Score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore of >1 point. CS-free remission is the proportion of patients receiving corticosteroids at baseline and who discontinued steroids and achieved clinical remission.
†Clinical remission was defined as a complete Mayo Score of ≤2 points and no subscore >1 point.
‡Humira® is a registered trademark of AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL. For information related to Humira®, please see AbbVie.com.
CS=corticosteroid; IV=intravenous; MAdCAM-1=mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1.
For adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn’s disease (CD).
Patients achieved rapid response and long-term remission in the GEMINI I trial1
Study Design1: Two randomized, double‑blind, placebo‑controlled studies enrolled adult patients with moderately to severely active UC who had failed at least 1 conventional therapy, including corticosteroids or immunomodulators and/or ≥1 anti‑TNFα therapy. In UC Trial I, patients were randomized (3:2) to receive ENTYVIO 300 mg or placebo by intravenous infusion at Weeks 0 and 2. In UC Trial II, patients receiving ENTYVIO who demonstrated clinical response at Week 6 (from UC Trial I or an open-label cohort) were randomized (1:1:1) to receive either ENTYVIO 300 mg every 8 weeks, ENTYVIO 300 mg every 4 weeks, or placebo every 4 weeks. The ENTYVIO Q4W dosing regimen did not demonstrate additional clinical benefit over the Q8W dosing regimen. The Q4W dosing regimen is not the recommended dosing regimen.
- Ulcerative Colitis Trials I and II were randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies that enrolled adult patients who had moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis and had failed ≥1 conventional therapy, including corticosteroids or immunomodulators and/or ≥1 anti-TNFα therapy.
- Concomitant aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, and immunomodulators were permitted. Corticosteroids were tapered after Week 6; in the United States, immunosuppressants were discontinued after induction.
IV=intravenously; Q4W=every 4 weeks; Q8W=every 8 weeks; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Not included in efficacy analysis.
†Clinical response=reduction in complete Mayo Score of ≥3 points and ≥30% from baseline with an accompanying decrease in rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1 point or absolute rectal bleeding subscore of ≤1 point. Not a study end point. Data includes responders from both blinded and open-label cohorts.
‡The ENTYVIO Q4W dosing regimen did not demonstrate additional clinical benefit over the Q8W dosing regimen and is not the recommended dosing regimen.
*Plus–minus values are means ±SD.
†P-values for the comparison in cohort 1 between the placebo group and the vedolizumab group are all greater than 0.05.
‡Race was self-reported.
§Mayo Clinic scores range from 0 to 12, with higher scores indicating more active disease.
||The partial Mayo Clinic score consists of the Mayo Clinic score minus the sigmoidoscopy subscore; range, 0 to 9, with higher scores indicating more active disease.
¶Data on fecal calprotectin were available for 857 patients: 139 receiving placebo, 213 receiving vedolizumab in cohort 1, 505 receiving vedolizumab in cohort 2, and 718 receiving vedolizumab in the combined cohorts.
#Immunosuppressants included azathioprine and mercaptopurine.
**Loss of response indicates that the patient had a response initially but subsequently did not have a response.
TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
GEMINI I trial primary end points
Overall population compared with placebo
ENTYVIO-treated patients achieved
rapid response and long-term
remission
Clinical response at Week 61*
Clinical remission at Week 521†
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; Q8W=every 8 weeks.
*Clinical response=reduction in complete Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30% from baseline with an accompanying decrease in rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1 point or absolute rectal bleeding subscore of ≤1 point.
†Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
GEMINI I trial secondary end points
Overall population compared with placebo
Rapid symptom relief as early as Week 61*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval.
*Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
Significantly more ENTYVIO-treated patients achieved visible mucosal
improvement at Week 6 compared with placebo1*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval.
*Visible mucosal improvement=Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 (normal or inactive disease) or 1 (erythema, decreased vascular pattern, mild friability).
Over half of ENTYVIO-treated patients achieved visible mucosal improvement at
Week 521,7*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; Q8W=every 8 weeks.
*Visible mucosal improvement=Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 (normal or inactive disease) or 1 (erythema, decreased vascular pattern, mild friability).
Nearly one third of ENTYVIO-treated patients achieved corticosteroid-free remission at Week 521,7*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; Q8W=every 8 weeks.
*Assessed in the subgroup of patients who were receiving corticosteroids at baseline and who were in clinical response at Week 6 (n=72 for placebo and n=70 for ENTYVIO Q8W). Corticosteroid-free clinical remission was defined as the proportion of patients in this subgroup who discontinued corticosteroids by Week 52 and were in clinical remission at Week 52.
GEMINI I TRIAL EXPLORATORY END POINTS
TNFα subgroup analyses compared with placebo
Not powered for statistical significance.
Clinical response at Week 61,6*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Clinical response=reduction in complete Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30% from baseline with an accompanying decrease in rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1 point or absolute rectal bleeding subscore of ≤1 point.
Clinical remission at Week 521,6*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; Q8W=every 8 weeks; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
Visible mucosal improvement at Week 61,6*
Visible mucosal improvement at Week 521,6*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; Q8W=every 8 weeks; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa=Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 (normal or inactive disease) or 1 (erythema, decreased vascular pattern, mild friability).
Corticosteroid-free remission at Week 521,6*
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; Q8W=every 8 weeks; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Assessed in the subgroup of patients who were receiving corticosteroids at baseline and who were in clinical response at Week 6 (n=72 for placebo and n=70 for ENTYVIO Q8W). Corticosteroid-free clinical remission was defined as the proportion of patients in this subgroup who discontinued corticosteroids by Week 52 and were in clinical remission at Week 52.
The Mayo score is used to assess the severity of ulcerative colitis7,8
The Mayo score consists of 4 factors:
- Physician Global Assessment
- Endoscopy findings
- Stool frequency
- Rectal bleeding severity
The Mayo Score ranges from 0-12, with higher scores
indicating more severe disease.
Demonstrating an effect on a composite multiple clinical
factor measure does not represent a clear effect on any of
the individual components.
- The 2 individual patient-reported components (stool frequency and rectal bleeding) are part of the Mayo score and were not powered for statistical significance
- Correlation of depicted PROs to Week 6 and Week 52 primary end points was not evaluated in the analysis
GEMINI I trial EXPLORATORY END POINTS: Patient-reported Outcomes
Overall population compared with placebo
Not powered for statistical significance.
Analysis of rectal bleeding subscore7*†‡
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Data are derived from a post-hoc analysis of Ulcerative Colitis Trial I and therefore not powered for statistical significance and should be considered exploratory.
†Patients with baseline rectal bleeding subscore=0 were excluded from the analysis.
‡Data points represent adjusted % change from baseline mean, where adjustment is for subscore baseline value and treatment.
Analysis of stool frequency subscore7*†‡
ENTYVIO IV
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Data are derived from a post-hoc analysis of Ulcerative Colitis Trial I and therefore not powered for statistical significance and should be considered exploratory.
†Patients with baseline stool frequency subscore=0 were excluded from the analysis.
‡Data points represent adjusted % change from baseline mean, where adjustment is for subscore baseline value and treatment.
In the first head-to-head study of biologics in UC
ENTYVIO: SUPERIOR to Humira® (adalimumab)
In clinical remission at Week 52 in the overall population2,3*†
VARSITY primary end point (overall population): ENTYVIO IV 31% (n=383) vs 23% (n=386) with Humira® (P=0.006; 95% CI: 3%, 15%)2
*Humira® is a registered trademark of AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL. For information related to Humira®, please see AbbVie.com.
†Clinical remission was defined as a complete Mayo Score of ≤2 points and no subscore >1 point.
Study Design2: VARSITY was a double‑blind, double‑dummy, active‑controlled trial that compared ENTYVIO with Humira® in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Eligible patients were randomized (1:1) to receive ENTYVIO and placebo, or Humira® and placebo. After induction, patients remained in their respective treatment group throughout the maintenance phase (treat-through design). Previous exposure to TNFα inhibitors other than Humira® was permitted in up to 25% of patients. Patients who had no response or lost response to conventional therapies were eligible. Dosing was consistent with the US product label for both ENTYVIO and Humira®; no dose escalation was permitted for either treatment group.
Review the breakthrough trial
VARSITY Trial Study Design
VARSITY was a double‑blind, double‑dummy, active‑controlled trial that compared ENTYVIO with Humira® in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.
- Eligible patients were adults (aged 18 to 85 years) with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis, defined as a complete Mayo score of 6 to 12 (range 0 to 12; higher scores represent more active disease), an endoscopic subscore of ≥2, colonic involvement of ≥15 cm, and a confirmed diagnosis of ulcerative colitis for ≥3 months. Anti-TNFα-naïve patients who had not responded or lost response to conventional treatments were eligible. Centrally read endoscopies were performed at Weeks 14 and 52
- Dosing was consistent with the US product label for both ENTYVIO and Humira®; no dose escalation was permitted for either treatment group. After induction, patients stayed in their treatment group throughout the maintenance phase (treat-through design)
- Enrollment of patients who discontinued treatment with an anti-TNFα (except adalimumab) due to documented reasons other than safety was capped at 25% (~21% was reached). Most of the trial population (97.3%) had moderately to severely active disease (Mayo score 6-12). Patients with mild disease represented significant protocol deviations. Per-protocol sensitivity analyses indicated no change from overall population results
- Patients naïve to anti-TNFα therapy were enrolled if they were failing current treatment (eg, CS, 5-ASA, or immunomodulators). Per-protocol sensitivity analyses indicated no change from overall population results. Patients on a 5-ASA or immunomodulator at baseline maintained stable doses throughout the study
*Includes 2 patients who enrolled in the trial but never received any study drug.
5-ASA=5-aminosalicylate; CS=corticosteroids; IV=intravenous; Q2W=every 2 weeks; Q8W=every 8 weeks; SC=subcutaneous; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Data on smoking status were missing for 2 patients in the ENTYVIO group.
†One patient in the Humira® group had ulcerative colitis of unknown duration.
‡Scores were available for 384 patients in the Humira® group and 380 patients in the ENTYVIO group.
§Data on fecal calprotectin were available for 332 patients in the Humira® group and 341 patients in the ENTYVIO group.
||The commonly used immunomodulators in the order of greatest to least were azathioprine, mercaptopurine, and methotrexate.
TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
VARSITY Trial Primary End Point
Overall population
ENTYVIO demonstrated
SUPERIORITY TO HUMIRA®
in clinical remission at Week 522*
Clinical remission2*
ENTYVIO IV
Humira® (adalimumab)
CI=confidence interval.
*Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
VARSITY trial secondary end points
Overall population
Differences you can see
ENTYVIO demonstrated superiority to Humira® in endoscopic improvement at Week 522*
ENTYVIO IV
Humira® (adalimumab)
CI=confidence interval.
*Endoscopic improvement was defined as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of ≤1 point.
Nonsignificant differences in corticosteroid-free remission at Week 529,10*
ENTYVIO IV
Humira® (adalimumab)
Approximately 36% of randomized patients were on corticosteroids at baseline.
CI=confidence interval.
*Corticosteroid-free clinical remission rates were assessed in patients who were receiving corticosteroids at baseline (as reported in electronic case report form). Corticosteroid-free clinical remission was defined as the population of patients in this subgroup who discontinued corticosteroids by Week 52 and were in clinical remission (defined as complete Mayo score ≤2 points and no subscore >1 point at Week 52). For patients on corticosteroids at baseline: Doses must have been stable for ≥2 weeks prior to the first dose and remained unaltered through Week 6. After Week 6, a nonfixed dose tapering was started upon achieving response. During tapering, patients could return to baseline doses only once for loss of response before repeating tapering. Per protocol, patients unable to taper were withdrawn from the study and considered treatment failures for each of the outcomes.
VARSITY trial exploratory end points
Overall population
Not powered for statistical significance.
Histologic remission2*†
Several definitions of histologic remission in ulcerative colitis have been described. There is no single gold standard for assessing histologic activity in ulcerative colitis, and none of the currently available histologic scoring indices have been fully validated.11-13
ENTYVIO IV
Humira® (adalimumab)
CI=confidence interval.
Robarts Histopathology Index Score (RHI) <3*
- RHI is a 4-item measurement that was developed using items from previously validated measurements of histologic change and includes signs of inflammation, epithelial changes, and/or erosions/ulcers11
- RHI score ranges from 0 (no disease activity) to 33 (severe disease activity)2
Geboes Score (GS) <2†
- GS is a 7-item measurement that assesses biopsied tissue for signs of histologic changes, which include structural changes, signs of inflammation, epithelial changes, and/or erosions/ulcers14
- GS is calculated by using a scale that ranges from 0 to 5.4, with higher scores indicating more severe disease activity2
*Histologic remission per RHI is defined as an RHI score <3.
†Histologic remission per Geboes score is defined as a GS <2.
Patients with missing histologic remission status were considered nonresponders.
Clinical response rates by visit based on change in partial Mayo score from baseline9,10*†
ENTYVIO IV
Humira® (adalimumab)
CI=confidence interval.
*Clinical response based on partial Mayo score is defined as a reduction in partial Mayo score of ≥2 points and ≥25% from baseline, with an accompanying decrease in rectal bleeding subscore (RBS) of ≥1 point or absolute RBS of ≤1 point. The partial Mayo score is a composite index of 3 disease activity variables (stool frequency, rectal bleeding, and Physician Global Assessment, each scored on a scale from 0 to 3 (higher scores indicate greater disease activity)). Partial Mayo score is calculated analogously to the complete Mayo score but excludes the sigmoidoscopy subscore.
†Full analysis set includes all randomized patients who received at least 1 dose of study drug.
‡Patients with missing clinical response status were considered nonresponders.
Clinical response based on Mayo score at Week 149,10*
ENTYVIO IV
Humira® (adalimumab)
CI=confidence interval; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Clinical response is defined as a reduction in Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30% from baseline with an accompanying decrease in rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1 point or absolute rectal bleeding subscore of ≤1 point. Patients with missing clinical response status were considered nonresponders.
VISIBLE 1 demonstrated that ENTYVIO offers a consistent clinical profile in UC
THE ENTYVIO YOU KNOW
NO MATTER HOW
IT’S DELIVERED
Individual results may vary.
Study Design1,15: A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial enrolled adult patients with moderately to severely active UC. At Week 6, patients who achieved clinical response were randomized to maintenance treatment with ENTYVIO SC + placebo IV, ENTYVIO IV + placebo SC, or placebo (IV and SC) in a 2:1:1 ratio, with stratification by concomitant CS use, clinical remission at Week 6, and previous anti-TNF failure or concomitant immunomodulator use. The ENTYVIO IV arm is a reference arm and not powered for statistical significance.
IV=intravenous; SC=subcutaneous
VISIBLE 1 Was a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Double-dummy, Multicenter, Placebo-controlled Trial
VISIBLE Study Details1,15
- Eligible patients were adults (aged 18 to 80 years) with moderately to severely active UC (defined as a total Mayo score of 6 to 12) for ≥6 months; an endoscopic score of ≥2; colonic involvement of ≥15 cm; an inadequate response to, loss of response to, or intolerance to ≥1 other treatment that was a CS, immunomodulator, and/or anti-TNF therapy; and a confirmed diagnosis of UC with histopathology
- At Week 6, patients were assessed for clinical response, defined as a reduction in total Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30% from Week 0 with an accompanying decrease in rectal bleeding score (RBS) of ≥1 point or absolute RBS of ≤1
- Patients with a clinical response at Week 6 were randomized to maintenance treatment with ENTYVIO SC + placebo IV, ENTYVIO IV + placebo SC, or placebo (IV and SC) in a 2:1:1 ratio, with stratification by concomitant CS use, clinical remission at Week 6, and previous anti-TNF failure or concomitant immunomodulator use
- Patients who did not achieve clinical response at Week 6 (n=139), received a third dose of ENTYVIO IV; of these, 79.1% (110/139) achieved clinical response at Week 14 (not included in efficacy analysis)
- The overall population included all randomized patients who received at least 1 dose of study drug. Maintenance treatment was initiated at Week 6 after the open-label induction phase
- All primary and secondary end points were assessed at Week 52
*Not a study endpoint. Data includes responders from an open-label cohort.
IV=intravenous; Q2W=every 2 weeks; Q8W=every 8 weeks; SC=subcutaneous; TNF=tumor necrosis factor.
*Data were collected using electronic case report forms.
†Data on corticosteroid use were collected using an interactive web response system at the time of patient randomization.
VISIBLE 1 Trial Primary End Point
Overall population compared with placebo
The ENTYVIO IV arm is a reference arm and not powered for statistical significance.
Patients treated with ENTYVIO subcutaneous (SC) injection achieved clinical remission at Week 52 vs placebo1,15*
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
CI=confidence interval.
*Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
VISIBLE 1 Trial Secondary End Points
Overall population compared with placebo
The ENTYVIO IV arm is a reference arm and not powered for statistical significance.
ENTYVIO SC demonstrated significantly greater rates of endoscopic improvement and durable clinical response at Week 52 vs placebo1,15*†
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; IV=intravenous; NS=not significant; SC=subcutaneous.
Due to rounding, some estimates of treatment difference may not correspond with the mathematical differences shown above.
*Endoscopic improvement was defined as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of ≤1 point.
†Durable clinical response was defined as a reduction in total Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30% from Week 0 with an accompanying decrease in RBS of ≥1 point or absolute RBS of ≤1 at both Weeks 6 and 52.
No statistically significant differences in durable clinical remission or CS-free clinical remission at Week 52 vs placebo15‡§
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
CS=corticosteroid.
‡Durable clinical remission was defined as a total Mayo score of ≤2 and no individual subscore >1 at both Weeks 6 and 52.
§CS-free remission was defined as patients using oral corticosteroids at Week 0 who have discontinued oral corticosteroids and are in clinical remission at Week 52.
VISIBLE 1 Trial Exploratory End Points
The ENTYVIO IV arm is a reference arm and not powered for statistical significance.
Clinical remission at Week 521*
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; TNFα=tumor necrosis factor alpha.
*Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
Endoscopic remission at Week 5215*
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
CI=confidence interval; CS=corticosteroid; IV=intravenous; SC=subcutaneous.
*Endoscopic remission=Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0.
Clinical remission at Week 52 by prior treatment failure15*
*Clinical remission=complete Mayo score of ≤2 points and no individual subscore >1 point.
The Mayo Score is used to assess the severity of
ulcerative colitis2,8
The Mayo Score consists of 4 factors:
- Physician Global Assessment
- Endoscopy findings
- Stool frequency
- Rectal bleeding severity
The Mayo Score ranges from 0-12, with higher scores
indicating more severe disease.
Demonstrating an effect on a composite multiple clinical
factor measure does not represent a clear effect on any of
the individual components.
- The 2 individual patient-reported components (stool frequency and rectal bleeding) are part of the Mayo Score and were not powered for statistical significance
VISIBLE 1 TRIAL EXPLORATORY END POINTS: PATIENT-REPORTED OUTCOMES
Partial Mayo Score and symptom subscores by study visit15*†
The ENTYVIO IV arm is a reference arm and not powered for statistical significance.
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
CI=confidence interval.
*Data are derived from a post-hoc analysis of the VISIBLE I Trial and therefore not powered for statistical significance and should be considered exploratory.
†The partial Mayo score is a composite index of 3 disease activity variables (stool frequency, rectal bleeding, and Physician Global Assessment, each scored on a scale from 0 to 3 (higher scores indicate greater disease activity.))
VISIBLE 1 TRIAL EXPLORATORY END POINTS: PHARMACOKINETICS
ENTYVIO PEN & IV
PROVIDE CONSISTENT
DRUG TROUGH LEVELS

PK data for IV and pen were not directly compared and do not imply efficacy or safety.
The ENTYVIO IV arm is a reference arm and not powered for statistical significance.
The PK of ENTYVIO in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency have not been studied.1
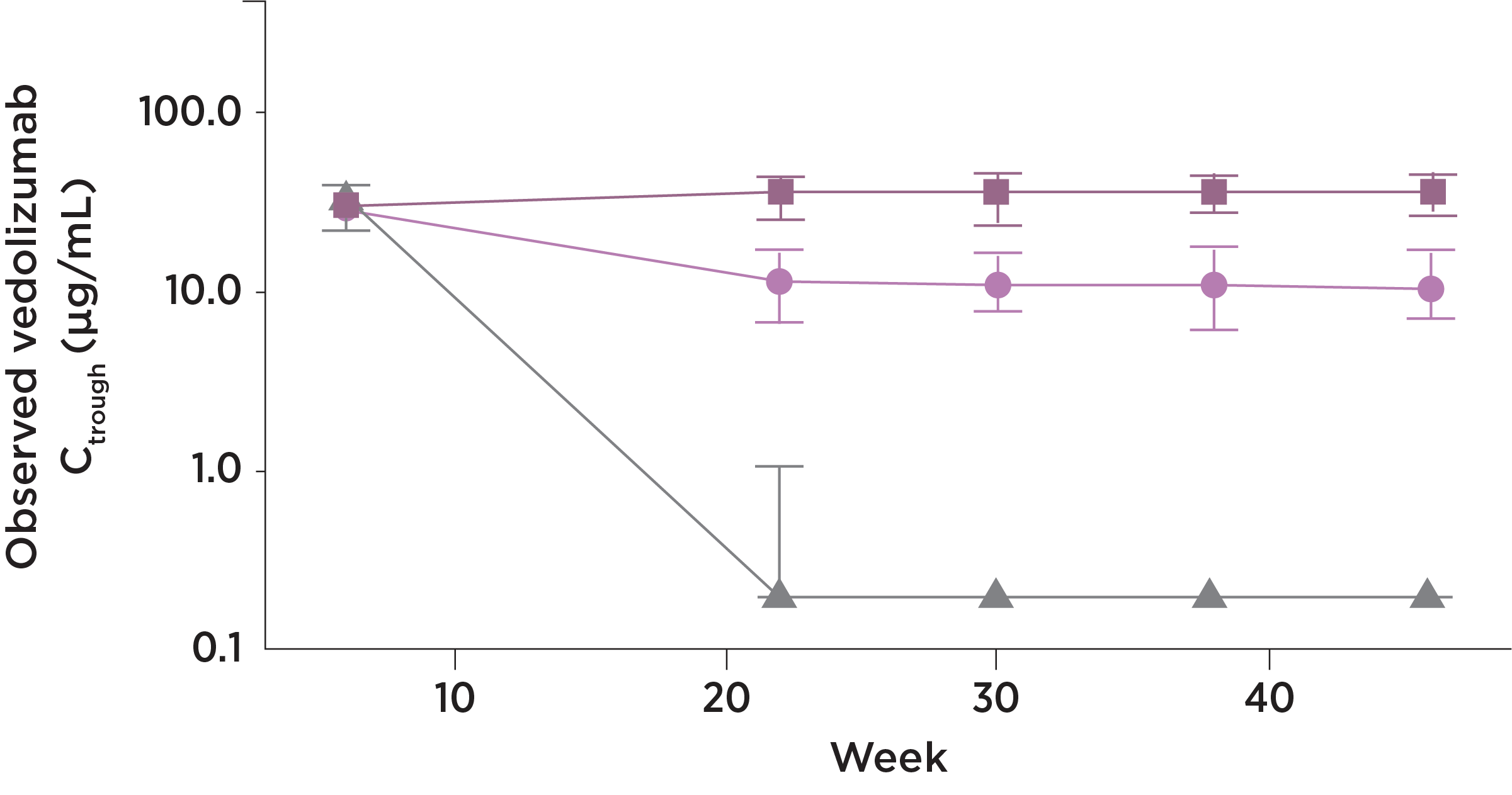
ENTYVIO trough levels with the SC and IV formulation15
ENTYVIO IV
ENTYVIO SC
Placebo
At steady state*, ENTYVIO
showed
Consistency
- The drug trough levels for the
ENTYVIO Pen were consistent
Stability
- The ENTYVIO Pen provided drug trough level stability for patients
No loss
- Transitioning to maintenance
therapy with the ENTYVIO Pen
did not lead to lower trough
levels
- Observed median and interquartile range trough concentrations (Ctrough) by study visit, presented on a semi-log scale (y-axis). Analysis set includes all randomized patients who received at least 1 dose of study drug and had sufficient blood sampling to allow for evaluation
- Blood samples for PK analyses were obtained within 30 minutes before dosing at study visits on Weeks 0, 6, 8, 14, 22, 30, 38, 46, and 50, and at any time during study visits at Weeks 7, 51, and 52
Vedolizumab SC dosing at 108 mg every 2 weeks was calculated to provide generally comparable drug exposure to that achieved with vedolizumab IV 300 mg every 8 weeks based on average serum vedolizumab concentrations at steady state. A previous population PK model was used to perform the simulations.
*The mean steady state serum trough concentration for the ENTYVIO Pen was 35.8 mcg/mL (SD ±15.2).
IV=intravenous; PK=pharmacokinetics; SC=subcutaneous.
Explore more topics
Support for patients prescribed ENTYVIO
Once you prescribe ENTYVIO, EntyvioConnect offers a range of programs
designed to help your patients in the way they need it most.
Review ENTYVIO's well-studied safety profile based on 4 clinical trials
See ENTYVIO results in Crohn’s disease
The content on this page has been written and
reviewed by Takeda.
References:
- ENTYVIO (vedolizumab) prescribing information. Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
- Sands BE, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Loftus EV Jr, et al. Vedolizumab versus adalimumab for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(13):1215-1226.
- Macaluso FS, Maida M, Grova M, et al. Head-to-head comparison of biological drugs for inflammatory bowel disease: from randomized controlled trials to real-world experience. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021;14:1-11.
- Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE, et al; for the GEMINI 1 Study Group. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(8):699-710.
- Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE, et al; for the GEMINI 1 Study Group. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(8):699-710 (supplemental appendix).
- Feagan BG, Rubin DT, Danese S, et al. Efficacy of vedolizumab induction and maintenance therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis, regardless of prior exposure to tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(2):229-239.e5.
- Feagan B, Lasch K, Lissoos T, et al. Rapid response to vedolizumab therapy in biologic-naïve patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(1):130-138. Published correction appears in Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(3):759.
- Schroeder KW, Tremaine WJ, Ilstrup DM. Coated oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis. A randomized study. N Engl J Med. 1987;317(26):1625-1629.
- Data on File. Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
- Sands BE, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Loftus EV Jr, et al. Vedolizumab versus adalimumab for moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(13):1215-1226.
- Pai R, Jairath V, Casteele NV, et al. The emerging role of histologic disease activity assessment in ulcerative colitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;88(6):887-898.
- Mosli MH, Parker CE, Nelson SA, et al. Histologic scoring indices for evaluation of disease activity in ulcerative colitis (review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5:1-39.
- Peyrin-Biroulet L, Sandborn W, Sands BE, et al. Selecting therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease (STRIDE): determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110(9):1324-1338.
- Mosli MH, Feagan BG, Zou G, et al. Development and validation of a histological index for UC. Gut. 2015;66(1):50-58.
- Sandborn WJ, Baert F, Danese S, et al. Efficacy and safety of vedolizumab subcutaneous formulation in a randomized trial of patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(3):562-572.e12.